The potential of gene editing for medical treatments and disease prevention
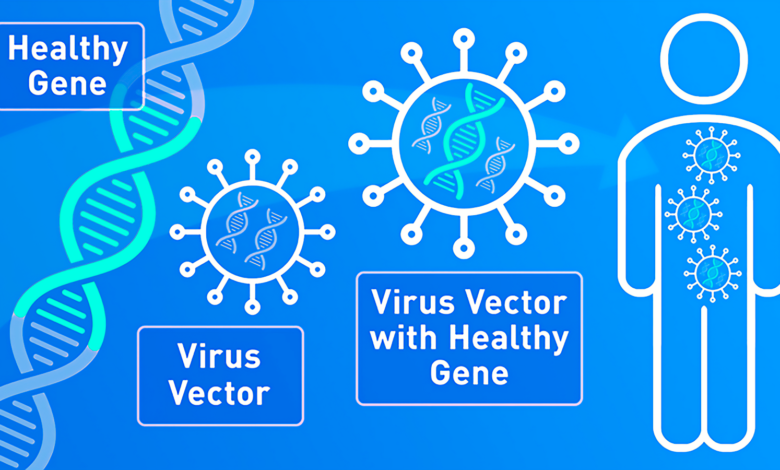
Gene editing has the potential to revolutionize the field of medicine by offering new treatments and preventative measures for various diseases. Gene editing is a technique that allows for precise modifications to be made to a person’s DNA, which can correct genetic mutations that cause diseases or even prevent diseases from occurring in the first place.
One of the most promising applications of gene editing is in the treatment of genetic diseases. These are diseases caused by mutations in a person’s DNA, which can lead to a wide range of symptoms and health problems. By using gene editing, scientists can potentially correct these mutations, restoring normal gene function and curing the disease.
Another potential application of gene editing is in disease prevention. By editing genes that are associated with certain diseases, it may be possible to prevent those diseases from occurring in the first place. For example, some genetic mutations are known to increase the risk of developing certain types of cancer. By editing these genes, it may be possible to reduce a person’s risk of developing those cancers.
Gene editing could also be used to enhance the immune system, making it better able to fight off diseases. By editing genes that control immune system function, scientists may be able to create more effective treatments for infectious diseases and other illnesses.
While the potential benefits of gene editing are clear, there are also many ethical and safety concerns that must be addressed. For example, some worry that gene editing could be used to create “designer babies” or to enhance certain traits, such as intelligence or athleticism. Others worry about the potential unintended consequences of gene editing, such as off-target effects or the creation of new diseases.
Despite these concerns, the potential of gene editing for medical treatments and disease prevention is enormous, and scientists are continuing to explore new ways to use this technology to improve human health.
In addition to genetic diseases, gene editing also has the potential to treat other types of illnesses. For example, scientists are exploring the use of gene editing to create new treatments for cancer, by modifying immune cells to better target and destroy cancer cells. Gene editing could also be used to create new treatments for infectious diseases, by editing genes in viruses or bacteria to make them less harmful or more susceptible to existing treatments.
One of the major advantages of gene editing is its precision. Unlike traditional drug treatments, which can affect many different parts of the body and have numerous side effects, gene editing can target specific genes and make precise modifications. This could lead to more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
Gene editing could also be used for personalized medicine, in which treatments are tailored to an individual’s unique genetic makeup. By sequencing a person’s DNA and identifying specific mutations or genetic markers associated with certain diseases, doctors could use gene editing to create personalized treatments that are more effective and less risky than traditional therapies.
However, there are also concerns about the safety and ethics of gene editing. One of the major concerns is the potential for unintended consequences or off-target effects, in which the gene editing process inadvertently modifies other genes or causes unexpected changes in a person’s DNA. Additionally, there are concerns about the ethical implications of gene editing, particularly with regard to its use in creating designer babies or enhancing certain traits.
Despite these concerns, gene editing holds enormous potential for medical treatments and disease prevention. As scientists continue to refine the technology and address safety and ethical concerns, gene editing could become a powerful tool for improving human health and extending life expectancy.



